What Two Other Terms May Used to Describe Alkanes
D the carbons in the para position of an aromatic have the same substituent groups. An alkane also known as paraffin is a saturated hydrocarbon with a single carbon-carbon bond.
Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry
After that the names are systematic like the words used to describe geometric shapes.
. When an extra bond is added forming a double bond the second bond is known as a pi bond. These use completely different sets of conditions. These are known as saturated hydrocarbons.
- involves high temp and pressure. Reactions of the free radicals lead to the various products. Alkane as saturated hydrocarbons.
417 describe how long-chain alkanes are converted to alkenes and shorter-chain alkanes by catalytic cracking using silica or alumina as the catalyst and a temperature in the range of 600700⁰C 418 explain why cracking is necessary in terms of the balance between supply and demand for different fractions. Alkanes with more than 35 C atoms tar are used. - carbon atom unpaired e-.
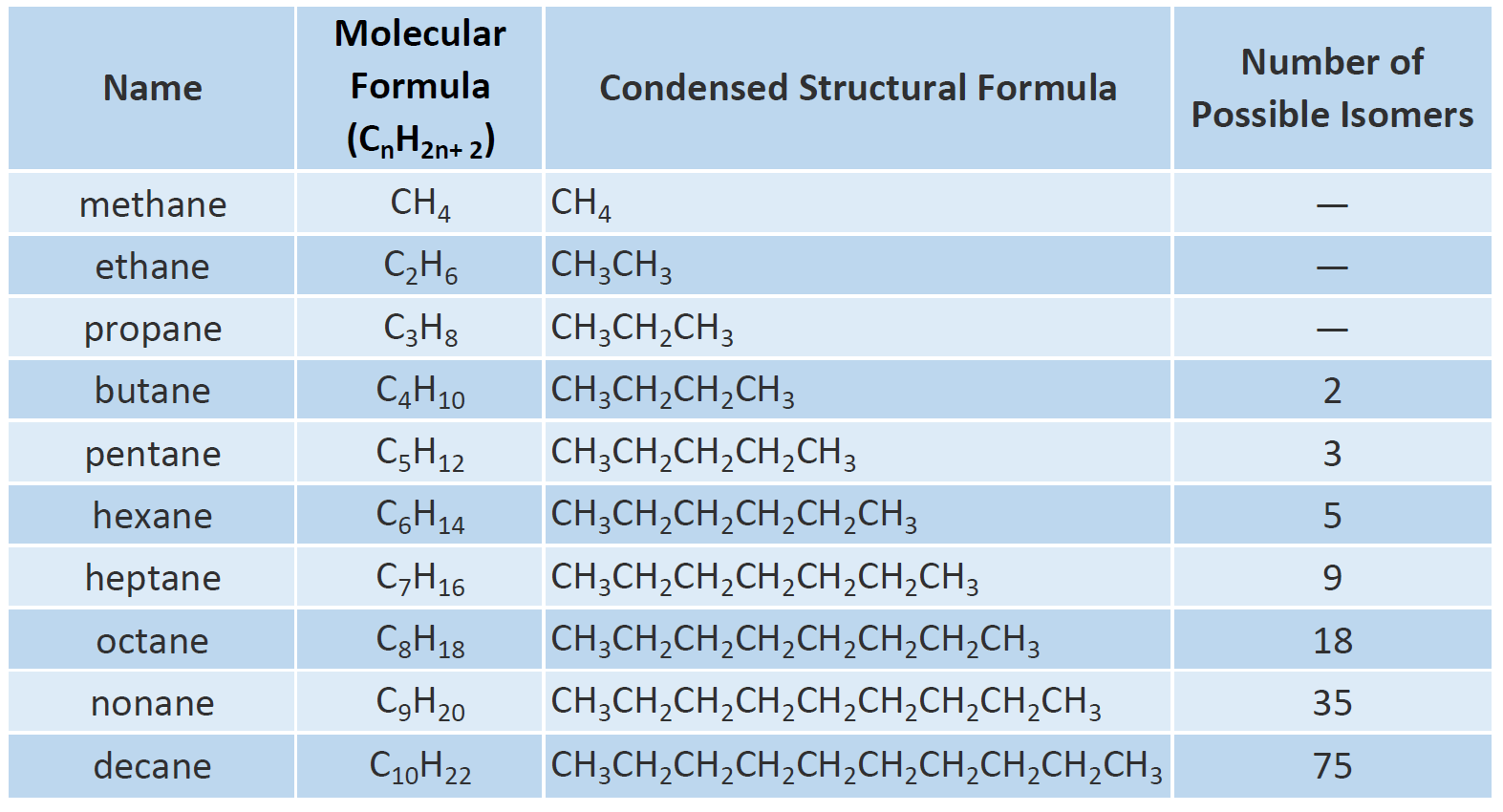
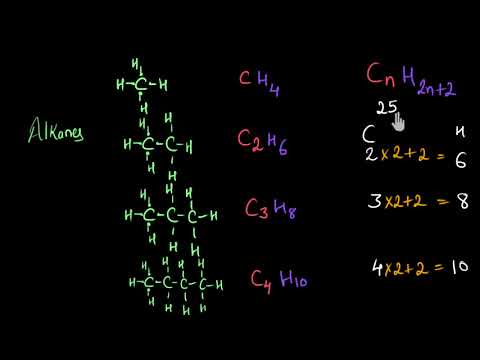
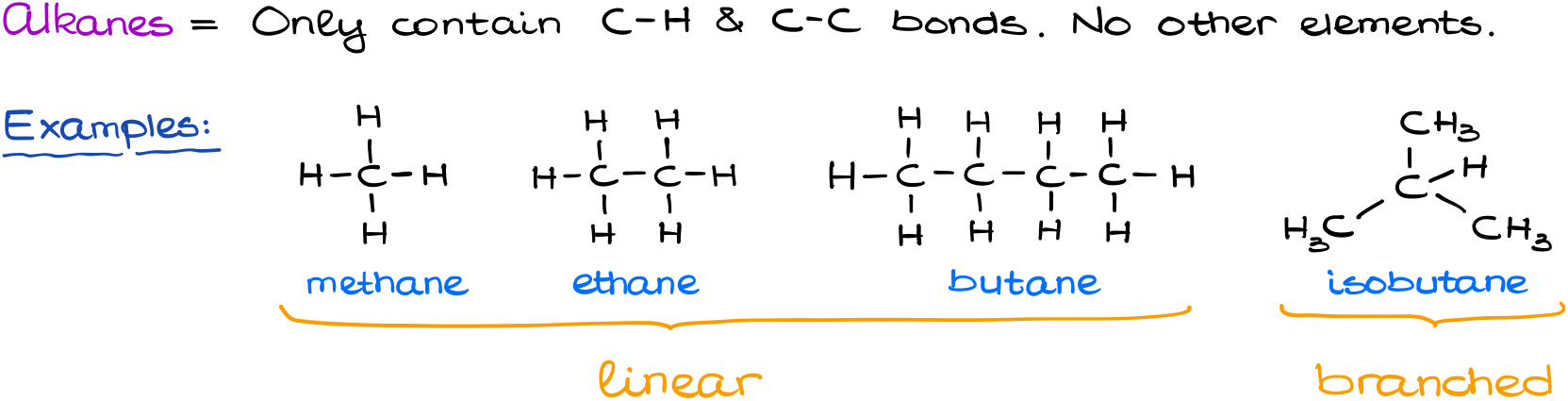
C_nH_2n2 The general formula means that the number of hydrogen atoms in an alkane is double the number of carbon atoms plus two. The commonly known types of alkanes are methane ethane and. Also comprises a homologous series having a molecular formula of CnH2n2.
Here there is only one carbon-carbon bond and the rotational structures rotamers that it may assume fall between two extremes staggered and eclipsedIn the following description of these conformers several structural notations are used. Catalyst Ni is used in finely divided form. Which compound is cis-12- Dimethylcyclohexane.
If Pt or Pd are used as catalyst reaction occurs at normal temperature. Their general formula is CnH2n2. For more on mastering alkanes and reactions use coupon code acespring to save 10 off.
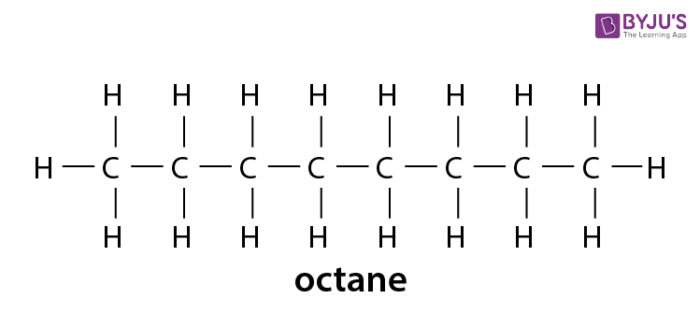
We looked at methane ethane and propane. Alkanes is hydrocarbon compound with one single bond. Carbons are bonded together in a chain-like structure.
Alkanes are a series of compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms with single covalent bonds. Petrol and other fuels are produced from it using fractional distillation. This group of compounds consists of carbon and hydrogen atoms with single covalent bonds.
Organic chemistry is the study of the structures and reactions of organic compounds mostly which contain covalent bonds and not forgetting other compounds such as nitrogen oxygen and hydrogen. This article focuses mainly on the acyclic alkanes and their properties and explains the differences. Secondary a hydrogen on a carbon attached to only TWO other carbons.
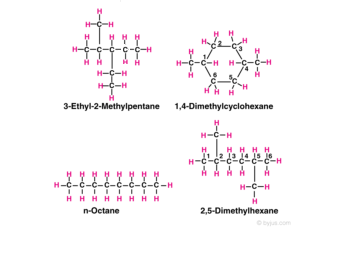
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. Using Common Names with Branched Alkanes. CH CH CH CH CH A a B b Cc D d 2.
Namely acyclic alkanes C n H 2n2 and cyclic alkanes C n H 2n. They possess a single bond between carboncarbon and carbonhydrogen atoms. Instead carbon-carbon bonds are broken so that each carbon atom ends up with a single electron.
Alkanccyclo 12- The most stable conformation of 12-dibromoethane is. Are examples of alkanes. B hydrogen is added to both of the carbon atoms in a double bond.
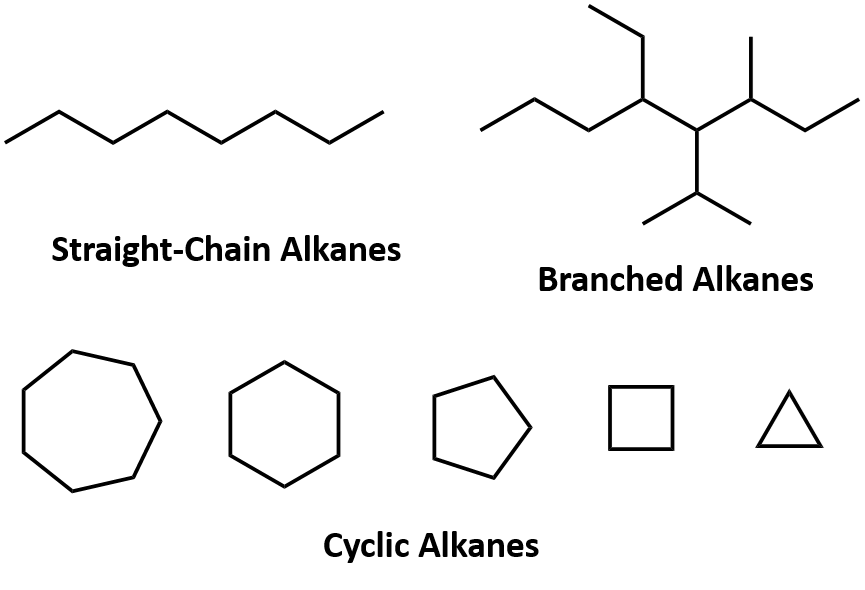
Some alkanes like the ones we have seen are straight-chain alkanes. Alkenes and alkynes on catatlytic hydrogenation give alkanes. Alkanes alkenes and alkynes are similar in name but they are slightly different.
H I II II IV V A I B II C III D IV E V 13. CH 2 CH 2 H 2 CH 3-CH 3. Ethane Conformations The simple alkane ethane provides a good introduction to conformational analysis.
The key difference between Alkanes and Alkenes is their chemical structure. First four alkanes are used as a fuel mainly for heating and cooking purpose. CHCH 2H 2 CH 3-CH 3.
There are two main molecular arrangements in Alkanes. - c-c bond breaks that one e- from pair in covalent bond goes to each c atom. Alkaneround Ringalkane Cycloalkane C.
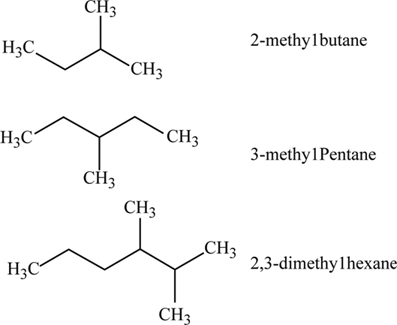
These common names make use of prefixes such as iso- sec- tert- and neo-The prefix iso- which stands for isomer is commonly given to 2-methyl alkanesIn other words if there is methyl group located on the second carbon of a. Crude oil is a finite resource. Alkanes vary with the molecular weight and the molecular structure.
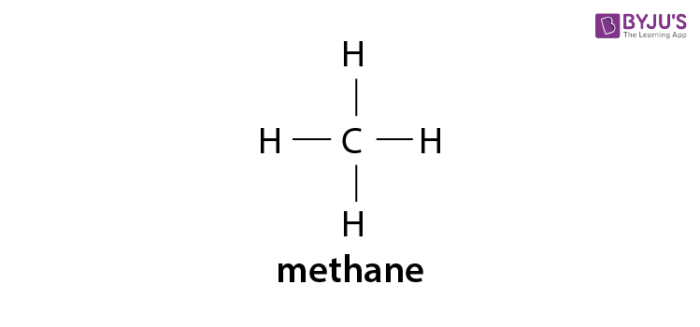
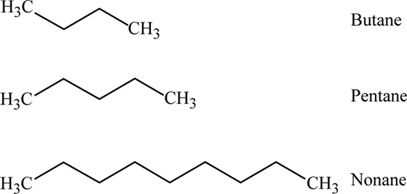
Here are more. The general formula is C n H 2n2. Methane ethane propane butane pentane etc.
The pi bond is much weaker than the sigma bond and breaks quite easily which is why alkenes are much more reactive than their fellow hydrocarbons. The first views the ethane molecule. In other words free radicals are formed.
Alkanes Hydrocarbons having no double or triple bond functional groups are classified as alkanes or cycloalkanes depending on whether the carbon atoms of the molecule are arranged only in chains or also in rings. Single covalent bonds are also known as sigma bonds. CNG petrol diesel are used as fuels for automobiles.
For example LPG and CNG. C the carbons in an alkene double bond each have two different substituent groups. Lower liquid alkanes are used as solvent.
Single bonded hydrocarbon atoms. Butane where but- tells us there are four carbons in the chain and hexane where hex- refers to the six carbons of the chain. The straight chain alkanes share the same general formula.
Tertiary a hydrogen on a carbon attached to THREE other carbons. Thermal cracking does not go via ionic intermediates like catalytic cracking. Cracking is used to convert long alkanes into shorter more useful hydrocarbons.
Eventhough the use of them may overlaps in some cases each of them is a compound on their own. A a branched alkane has a halogen added to two adjacent carbon atoms. Suffix ane is added at the end of the name of each alkane.
As for the alkenes it has for the very least double bonds compared to alkanes single bond. 11 What is the general term used to describe an alkane in a ring structure. Alkanes are also called saturated hydrocarbons whereas hydrocarbons that contain multiple bonds alkenes alkynes and aromatics are unsaturated.
The acyclic saturated hydrocarbons are called paraffins since they are relatively unreactive towards most of the reagents such as acids bases oxidizing and reducing agents. It gives the description of chemical and physical properties of Alkanes. In the IUPAC system they are called alkanes.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with the general molecular formula of C n H 2n2 and alkenes are said to be an. The names of the 4 simplest alkanes are methane ethane propane and butane. Key Difference Alkanes vs Alkenes Alkanes and Alkenes are two types of hydrocarbon families which contain carbon and hydrogen in their molecular structure.
Answer 1 of 5. Certain branched alkanes have common names that are still widely used today. These organic compounds are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms.

Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry

Hydrocarbons Chemistry Atoms First
Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry

Naming Alkanes With Practice Problems Chemistry Steps

Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes
Organic Chemistry Structure Of Alkanes Introduction To Organic Molecules Sparknotes
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes

Alkanes An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes General Molecular Formula Video Khan Academy
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes
Organic Chemistry Structure Of Alkanes Introduction To Organic Molecules Sparknotes

Learn About Alkanes In Organic Chemistry Chegg Com
Definition Of Alkanes Chegg Com
Definition Of Alkanes Chegg Com

Alkanes Formula List Structure Definition Examples Videos
Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry

Comments
Post a Comment